What Is Blockchain? A Simple Explanation for Complete Beginners
Blockchain is often described using heavy technical jargon. This article breaks everything down using real-world analogies, simple visuals, and clear examples so anyone can understand how it works — even with zero technical background.
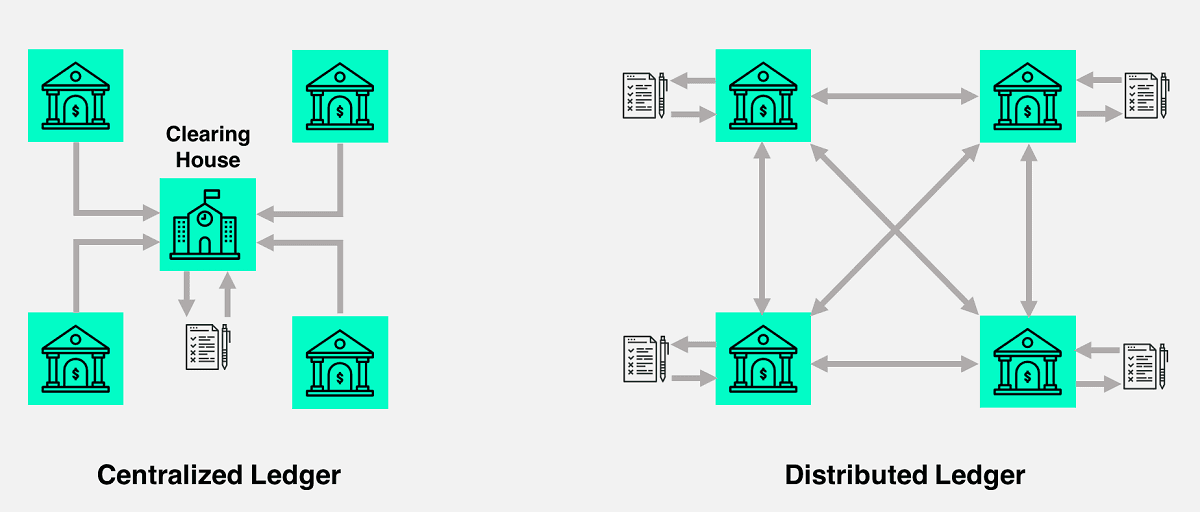
Think of blockchain as a special type of digital notebook that is shared among thousands of computers. Once something is written in this notebook, it becomes extremely difficult to erase, cheat, or modify. This creates trust — not because people are honest, but because the system itself makes cheating nearly impossible.
Blockchain = Shared Digital Ledger
The easiest way to understand blockchain is through a familiar analogy:
Imagine a group of friends who share a notebook.Every time someone spends or receives money, they write it down. Everyone has a copy of this notebook, so cheating becomes extremely hard.
- No one can erase past entries — everyone would notice immediately.
- No one can fake an entry — others won’t accept a page that doesn’t match their copy.
- Everyone stays in sync — new pages are shared instantly with the entire group.
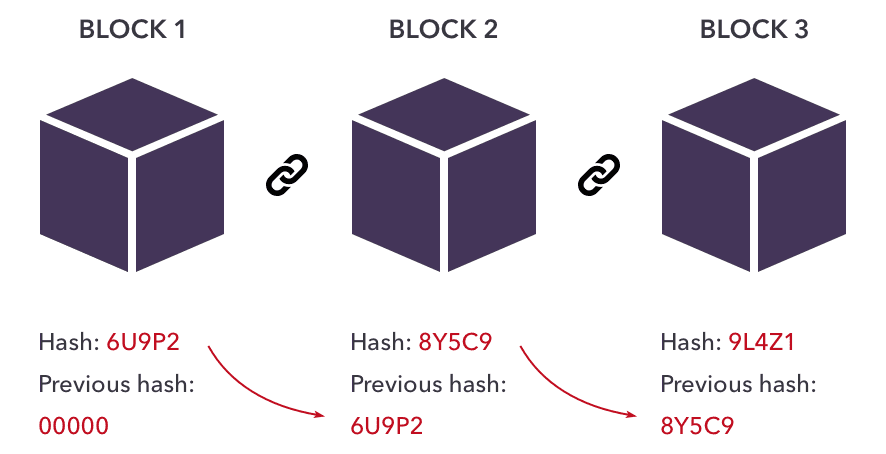
What Is a "Block"?
A block is basically a page in the notebook. But unlike a normal page, each block has three special pieces of information:
- 1. The transactions — the notes written on the page.
- 2. A timestamp — when the page was added.
- 3. A unique fingerprint called a “hash”
A hash is like a digital barcode generated from the contents of the page. If you change even a single letter, the barcode becomes completely different.
Each block also stores the hash of the previous block and then hashes the whole block along with the previous block hash. This is what forms a chain.
Because blocks are linked like this, modifying anything in an old block would break every block that comes after it — making tampering mathematically impossible to hide.
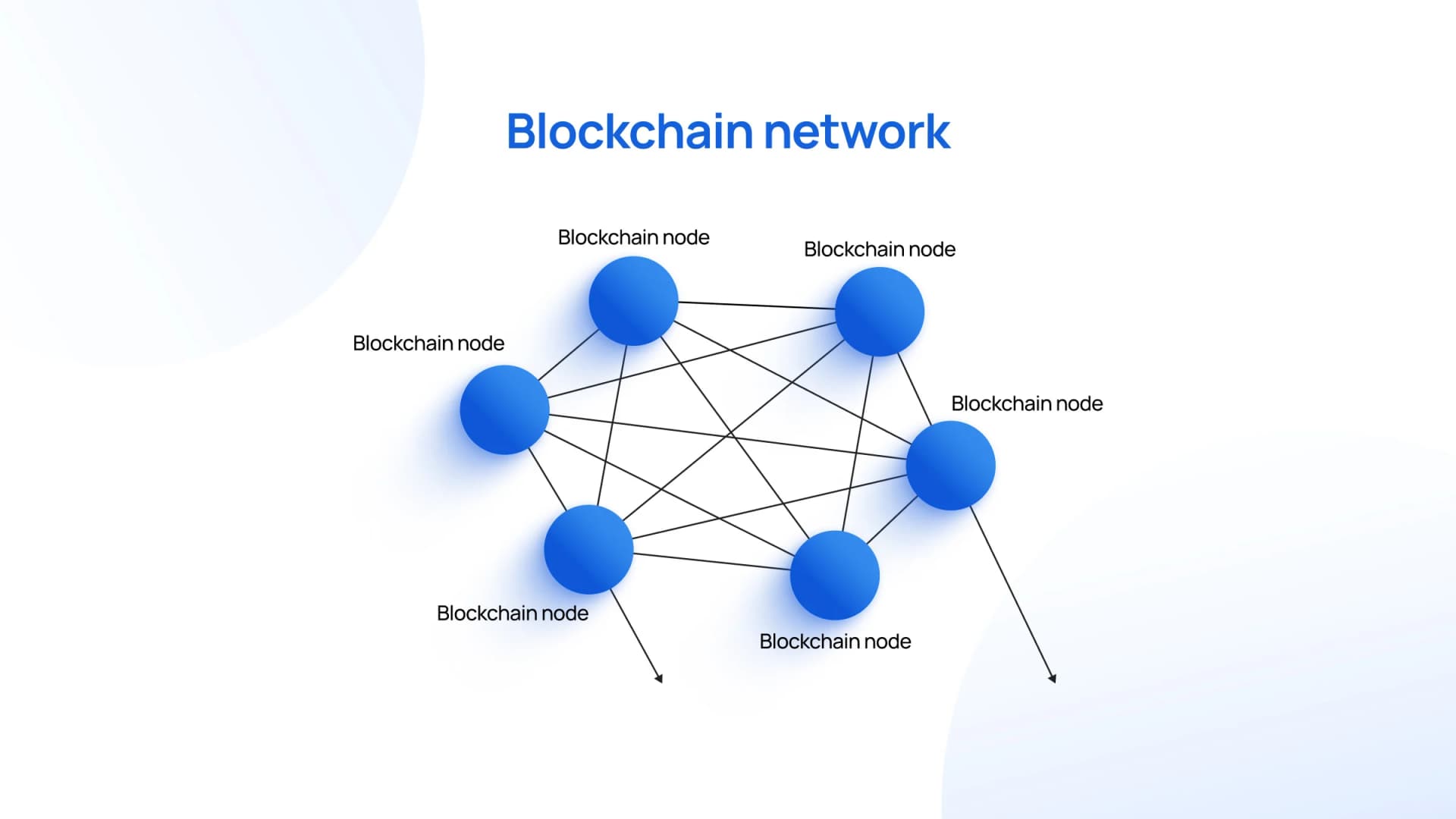
How Does Blockchain Stay Secure?
Instead of a bank or single authority checking everything, blockchain relies on a network of participants called validators or miners.
Continuing our notebook analogy:
Validators are like referees who review each new page to confirm all the entries are valid before adding it to the notebook.
In Bitcoin, miners compete to solve a mathematical puzzle. The winner adds the next block and earns newly-created Bitcoin as a reward. This system is called Proof of Work.
Other blockchains use Proof of Stake, which uses far less energy.
Where Does Bitcoin Fit In?
Bitcoin was the first major application of blockchain technology. It is a digital currency that doesn’t rely on banks. Instead, ownership and transactions are tracked entirely through the blockchain ledger.
In simple words:
- Bitcoin = money
- Blockchain = the technology used to track the money safely
So blockchain is not “Bitcoin” — it is a technology that Bitcoin uses.
Why Is Blockchain Valuable?
Blockchain lets people trust the information they are using — even if they don’t trust each other. This removes the need for middlemen like banks or brokers.
- Security: Old records can't be secretly altered.
- Transparency: Anyone can verify transactions.
- Ownership: You fully control your assets.
- Efficiency: Cheaper and faster than manual verification.
Want to Learn More?
Here are beginner-friendly resources to explore blockchain further: